 Unexplored actions of Veklury® (remdesivir) formulations against SARS-CoV-2 infection due to their cyclodextrin content
Unexplored actions of Veklury® (remdesivir) formulations against SARS-CoV-2 infection due to their cyclodextrin content
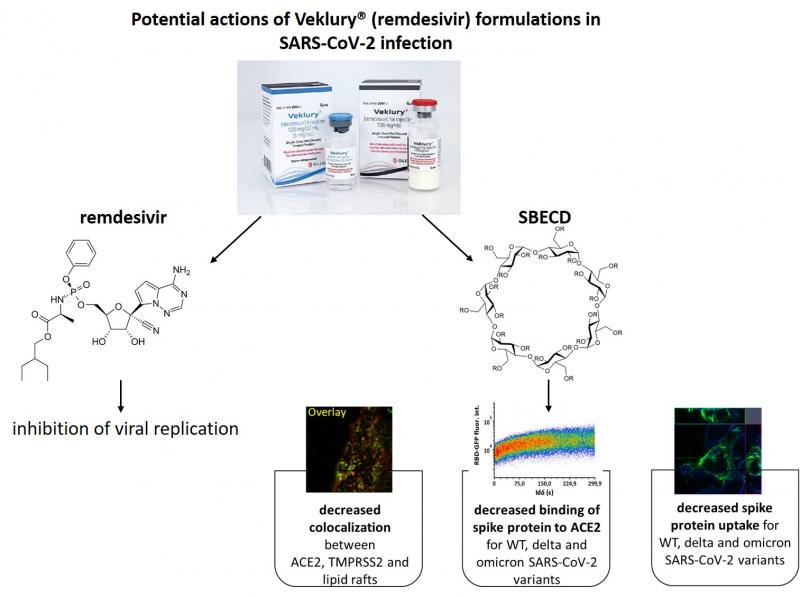
Remdesivir, under the trade name Veklury®, was the first approved drug for the treatment of severe COVID-19 disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and is still used in clinical practice as powder or concentrated solution formulations for intravenous infusion. Since the solubility of remdesivir is very poor, in addition to the same amount of remdesivir, both formulations contain also large, but different amounts of the carrier, sulfobutylether-beta-cyclodextrin (SBECD), which can lead to very high vehicle concentrations in serum during the treatment of the disease.
Tamas Kovacs, Kitti Kurtan, Zoltan Varga, Peter Nagy, Gyorgy Panyi and Florina Zakany from the Department of Biophysics and Cell Biology at the Faculty of General Medicine, University of Debrecen, were the first who demonstrated that SBECD, thought to be an inert carrier in Veklury® formulations, also has active antiviral effects. SBECD, just like other cyclodextrins, is able to interact with the cell membrane and disrupt cholesterol-rich lipid rafts despite even when complexed in formulations. Lipid rafts serve as entry points for SARS-CoV-2, as they are preferentially accumulate ACE2 that is responsible for the binding and uptake of the viral spike protein. Consequently, these processes are also inhibited by the destruction of the lipid rafts in response to Veklury® or cyclodextrins treatments. Accordingly, in flow cytometry measurements, cholesterol-depleting cyclodextrins and Veklury® formulations dose-dependently reduced ACE2 binding of fluorescently labeled Wuhan-Hu-1, delta and omicron variant spike proteins, and, similarly, the uptake of spike proteins as assessed by confocal microscopy and three-dimensional quantitative image analysis.
With these experiments the authors have described novel potential antiviral effects of Veklury® formulations that not only inhibit the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of the virus, and thus its cellular replication due to their remdesivir content, but also reduce its cellular uptake due to their SBECD content. Further emphasizing the clinical relevance of their findings, the authors highlighted the potential benefits of applying Veklury® in a solution formulation due to its twice higher SBECD content and they also raised the possibility of using well-tolerable cyclodextrins as an adjuvant therapy in COVID-19.
The study was published in a prestigious international scientific journal, the British Journal of Pharmacology .
Tamas Kovacs, Kitti Kurtan, Zoltan Varga, Peter Nagy, Gyorgy Panyi, Florina Zakany
DOI: 10.1111/bph.16063