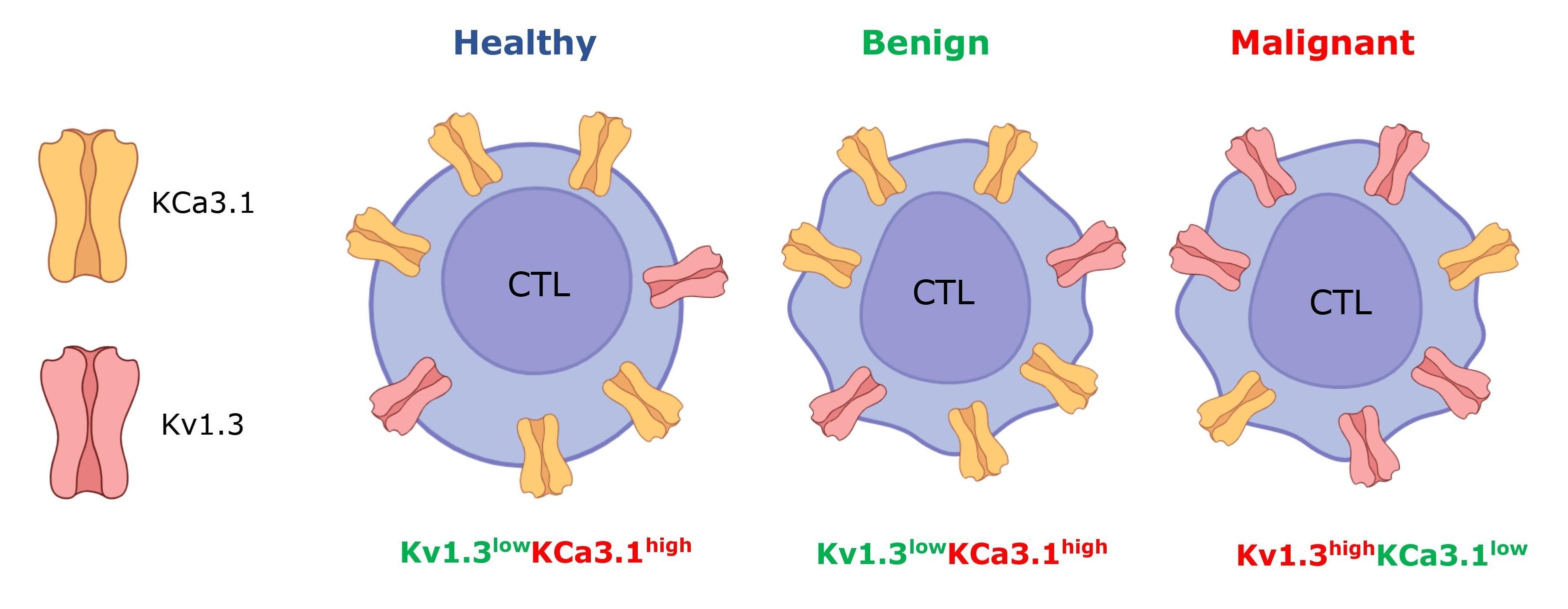
Vivien Jusztus, Péter Hajdu, and their colleagues in collaboration with the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the University of Debrecen studied the activity of potassium channels in CD8+ T lymphocytes. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) or CD8+ T cells play a role in the elimination of tumor cells. Ion channels control the Ca2+-dependent function of CD8+ lymphocytes such as cytokine/granzyme production and tumor killing. Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 K+ channels stabilize the negative membrane potential of T cells to maintain Ca2+ influx through CRAC channels. Electrophysiological measurements showed that the expression level of Kv1.3 was higher while the KCa3.1 activity was lower in CTLs from patients with malignant tumors as compared to healthy or benign tumor groups (see figure). They demonstrated that the CRAC-dependent Ca2+-response in malignant tumor patients’ CTLs was elevated compared to two other groups. They proposed that altered Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 expression in CTLs in ovarian cancer could serve as a biomarker in diagnostics and prognosis, and the increased Ca2+ response through CRAC channels may contribute to impaired CTL function. The findings of this study were published in the International Journal of Molecular Science (MDPI).